Scalability & Latency
average of 1.58ms and p99 of 4ms for 150 parallel clients sending 95,228 requests per second
MockServer is build to support massive scale from a single instance:
- Apache Benchmark tested up to 6,000 parallel clients and shows MockServer has an average of 1.58ms and p99 of 4ms for 150 parallel clients sending 95,228 requests per second
- Locust tested up to 3,000 parallel clients and shows MockServer has a p99 of 4ms for 150 parallel clients
Both performance testing frameworks show similar results up to 2,000 parallel clients at which point Locust reports warnings and the figures are no longer consistent with Apache Benchmark.
The following frameworks & techniques are used to maximise scalability:
- Netty an asynchronous event-driven network application framework to maximise the scalability of HTTP and TLS
- LMAX Disruptor a high performance inter-thread messaging library to maximise the scalability of recording events (i.e. state) and logging
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor a thread pool that can scheduled delayed tasks is used to execute delay response to avoid blocking threads
Performance Tests
MockServer has been performance tested using Apache Benchmark and Locust with the following scenario:
- four basic expectations, including method, path and headers
- basic GET request matching third expectation (i.e. three matches are attempted for each request)
During the test MockServer was run on a Java 13 JVM, with the following command:
java -Xmx500m -Dmockserver.logLevel=WARN -Dmockserver.disableSystemOut=true -jar ~/.m2/repository/org/mock-server/mockserver-netty/5.11.1-SNAPSHOT/mockserver-netty-5.11.1-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar -serverPort 1080The following graph shows how the p99 increases as the number of parallel clients increase.
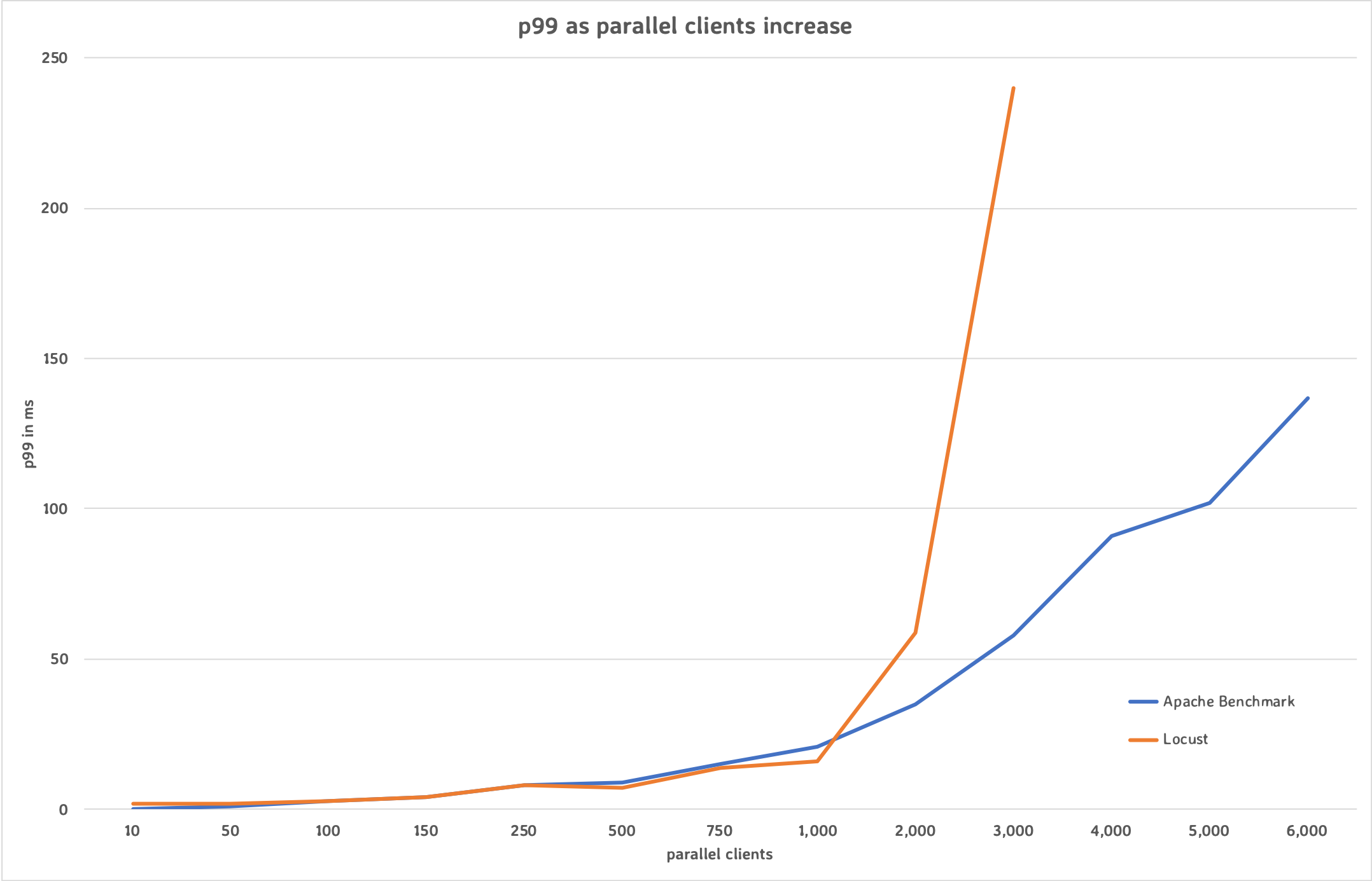
Apache Bench Performance Test Results
Apache Benchmark was executed as follows:
ab -k -n 10000000 -c <parallel clients> http://127.0.0.1:1080/simpleThe test results are:
| parallel clients | 50% | 66% | 75% | 80% | 90% | 95% | 98% | 99% | requests/s | mean | |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 77,122 | 0.13 | |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 85,765 | 0.58 | |
| 100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 92,846 | 1.08 | |
| 150 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 95,228 | 1.58 | |
| 250 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 86,470 | 2.89 | |
| 500 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 83,209 | 6.01 | |
| 750 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 75,554 | 9.93 | |
| 1000 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 21 | 75,423 | 13.26 | |
| 2000 | 24 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 29 | 31 | 35 | 82,191 | 24.33 | |
| 3000 | 37 | 39 | 40 | 40 | 43 | 46 | 51 | 58 | 78,171 | 38.38 | |
| 4000 | 52 | 55 | 57 | 59 | 64 | 70 | 82 | 91 | 73,552 | 54.38 | |
| 5000 | 65 | 67 | 70 | 71 | 75 | 79 | 90 | 102 | 74,065 | 67.51 | |
| 6000 | 80 | 84 | 88 | 90 | 97 | 104 | 122 | 137 | 70,432 | 85.19 |
Locust Performance Test Results
Apache Benchmark was executed as follows:
locust --loglevel=WARNING --headless --only-summary -u <parallel clients> -r 100 -t 180 --host=http://127.0.0.1:1080The test results are:
| parallel clients | 50% | 66% | 75% | 80% | 90% | 95% | 98% | 99% | 99.90% | 99.99% | requests/s | mean |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 11 | 0 |
| 50 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 50 | 0 |
| 100 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 100 | 0 |
| 150 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 149 | 0 |
| 250 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 15 | 46 | 245 | 2 |
| 500 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 46 | 479 | 2 |
| 750 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 29 | 34 | 699 | 3 |
| 1000 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 36 | 52 | 909 | 3 |
| 2000 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 12 | 22 | 34 | 49 | 59 | 87 | 110 | 1626.14 | 8 |
| 3000 | 51 | 78 | 99 | 110 | 160 | 180 | 220 | 240 | 290 | 310 | 2629.92 | 54 |
The following locustfile.py was used
import locust.stats
from locust import task, between
locust.stats.CONSOLE_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC = 60
from locust.contrib.fasthttp import FastHttpLocust
class UserBehavior(FastHttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 1)
@task
def request(self):
self.client.get("/simple", verify=False)
Clustering MockServer
MockServer supports a very high request throughput, however if a higher request per second rate is required it is possible to cluster MockServer so that all nodes share expectations.
Although expectations are clustered, currently there is no support for clustering the MockServer log therefore request verifications will only work against the node that received the request.
To create a MockServer cluster all instances need to:
- share a read-write file system i.e. same physical / virtual machine, NFS, AWS EFS, Azure Files, etc
- configure identical expectation initialiser and expectation persistence
- bind to a free port i.e. separate ports if on same physical / virtual machine
Each node could be configured as follows (adjusting the port as necessary):
MOCKSERVER_WATCH_INITIALIZATION_JSON=true \
MOCKSERVER_INITIALIZATION_JSON_PATH=mockserverInitialization.json \
MOCKSERVER_PERSIST_EXPECTATIONS=true \
MOCKSERVER_PERSISTED_EXPECTATIONS_PATH=mockserverInitialization.json \
java -jar ~/Downloads/mockserver-netty-5.11.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar -serverPort 1080 -logLevel INFOor
java \
-Dmockserver.watchInitializationJson=true \
-Dmockserver.initializationJsonPath=mockserverInitialization.json \
-Dmockserver.persistExpectations=true \
-Dmockserver.persistedExpectationsPath=mockserverInitialization.json \
-jar ~/Downloads/mockserver-netty-5.11.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar -serverPort 1080 -logLevel INFOScalability Configuration:
Number of threads for main event loop
These threads are used for fast non-blocking activities such as:
- reading and de-serialise all requests
- serialising and writing control plane responses
- adding, updating or removing expectations
- verifying requests or request sequences
- retrieving logs
Expectation actions are handled in a separate thread pool to ensure slow object or class callbacks and response / forward delays do not impact the main event loop.
Type: int Default: maximum of 35 or available processors count
Java Code:
ConfigurationProperties.nioEventLoopThreadCount(int count)System Property:
-Dmockserver.nioEventLoopThreadCount=...Environment Variable:
MOCKSERVER_NIO_EVENT_LOOP_THREAD_COUNT=...Property File:
mockserver.nioEventLoopThreadCount=...Example:
-Dmockserver.nioEventLoopThreadCount="20"Number of threads for the action handler thread pool
These threads are used for handling actions such as:
- serialising and writing expectation or proxied responses
- handling response delays in a non-blocking way (i.e. using a scheduler)
- executing class callbacks
- handling method / closure callbacks (using web sockets)
Type: int Default: maximum of 20 or available processors count
Java Code:
ConfigurationProperties.actionHandlerThreadCount(int count)System Property:
-Dmockserver.actionHandlerThreadCount=...Environment Variable:
MOCKSERVER_ACTION_HANDLER_THREAD_COUNT=...Property File:
mockserver.actionHandlerThreadCount=...Example:
-Dmockserver.actionHandlerThreadCount="20"Number of threads for each expectation with a method / closure callback (i.e. web socket client) in the org.mockserver.client.MockServerClient
This setting only effects the Java client and how requests each method / closure callbacks it can handle, the default is 5 which should be suitable except in extreme cases.
Type: int Default: 5
Java Code:
ConfigurationProperties.webSocketClientEventLoopThreadCount(int count)System Property:
-Dmockserver.webSocketClientEventLoopThreadCount=...Environment Variable:
MOCKSERVER_WEB_SOCKET_CLIENT_EVENT_LOOP_THREAD_COUNT=...Property File:
mockserver.webSocketClientEventLoopThreadCount=...Example:
-Dmockserver.webSocketClientEventLoopThreadCount="20"The the minimum level of logs to record in the event log and to output to system out (if system out log output is not disabled). The lower the log level the more log entries will be captured, particularly at TRACE level logging.
Type: string Default: INFO
Java Code:
ConfigurationProperties.logLevel(String level)System Property:
-Dmockserver.logLevel=...Environment Variable:
MOCKSERVER_LOG_LEVEL=...Property File:
mockserver.logLevelThe log level, which can be TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, OFF, FINEST, FINE, INFO, WARNING, SEVERE
Example:
-Dmockserver.logLevel="DEBUG"Disable logging to the system output
Type: boolean Default: false
Java Code:
ConfigurationProperties.disableSystemOut(boolean disableSystemOut)System Property:
-Dmockserver.disableSystemOut=...Environment Variable:
MOCKSERVER_DISABLE_SYSTEM_OUT=...Property File:
mockserver.disableSystemOut=...Example:
-Dmockserver.disableSystemOut="true"